A Compressor Map in
AFT Arrow allows you to more accurately model the full range of operating conditions for a Centrifugal Compressor junction. AFT recognized the need for this specific feature from customers via support requests and consulting projects. Well, good news…this capability is here! The feature was designed with the engineering design process in mind. AFT engineers even consulted industry experts during development to ensure it is a valuable addition to our powerful suite of compressible flow software.
What is a Compressor Map?
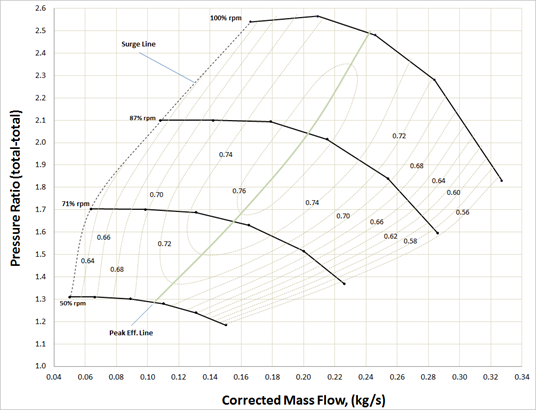
Compressors operating at a fixed speed are typically characterized by a Compressor Curve that relates the mass or volumetric flowrate to the compression ratio or rise in pressure/isentropic head. A Compressor Map is a family or collection of these curves for various speeds. However, Compressor Maps typically relate a corrected or non-dimensional mass flowrate on the x-axis to a pressure ratio on the y-axis. Furthermore, the speed is usually a corrected or non-dimensional speed. The boundaries of the Compressor Map define an entire range of possible operation. The left boundary is called the Surge Line, and the right boundary is called the Stall Line. These are limits that should be avoided, and Arrow has built-in Warnings that will be displayed if you are operating outside these boundaries of the Compressor Map.
Benefits of Using a Compressor Map
- Create alternate scenarios of the model faster
- Arrow linearly interpolates between the entered curves to find the operating point conditions
- Account for different inlet temperatures and pressures
- Input manufacturer data into Arrow more easily
Limitations of the Compressor Map
- The working fluid of the AFT Arrow model must be the same as the fluid used by the manufacturer when developing the Compressor Map
- The units must be provided in non-dimensional or corrected mass flowrate vs pressure ratio
How to Add a Compressor Map
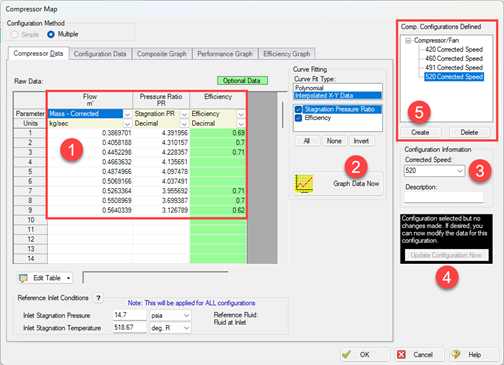
Open the Compressor Properties window, select the Centrifugal Compressor option, and select the radio button for Compressor Map. Then, click Enter Curve Data:- Enter the data for one of the curves and select the appropriate units from the column headers
- Click Graph Data Now (if you are using a polynomial curve fit, ensure that the curve fit closely matches the data)
- Enter the corrected or non-dimensional speed
- Click Update Configuration Now
- Click Create and repeat the process for the next curve