
Calculate steady-state pressure drop and flow distribution in liquid and low-velocity gas piping systems
Significantly improve the quality of systems engineering you can achieve, leading to less costly, more efficient, and more reliable piping systems.
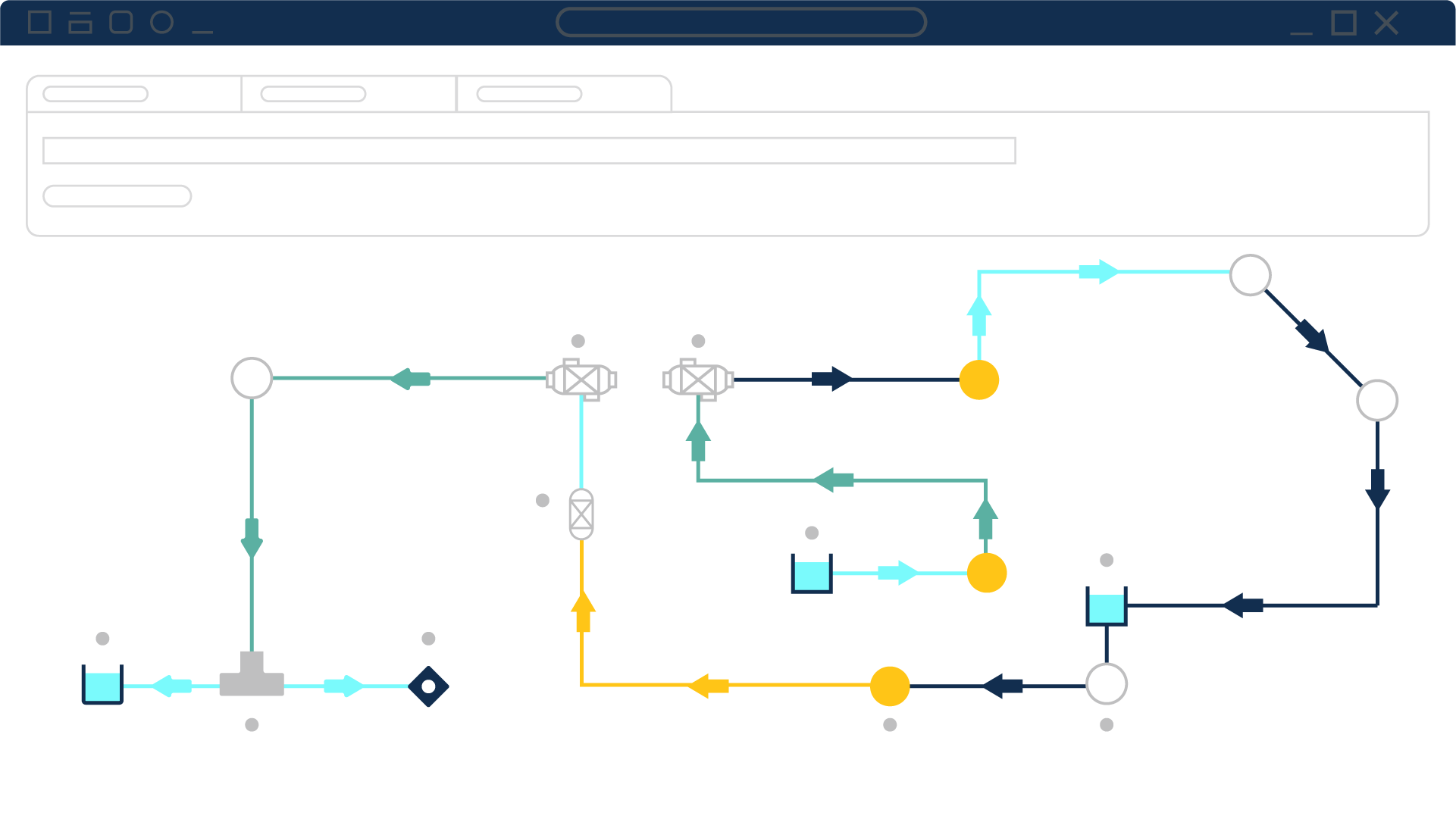
















You need accuracy
Quickly build, view, and validate complex pipe networks—all in a single intuitive graphical environment
Track and compare multiple design or operating cases within one file, enabling rapid “what‑if” comparisons
Automated Network Sizing calculates capital costs (pipes, components) or ongoing energy use to help optimize designs for both initial budget and lifecycle efficiency
Supports complex fluids and systems—including non‑Newtonian slurries, variable‑speed pumps, heat transfer, and goal‑seeking controls—making it ideal for rigorous engineering applications
Developed by engineers, for engineers
Scenario & system management
Track and compare multiple design cases, operating conditions, and system states with powerful tools in a single environment.
- Track all your design variants and potential operating conditions in a single file with Scenario Manager
- Use integrated, customizable graphing and reporting to make analysis visually intuitive
- Integrate with Excel to import model data and export output data
- Import piping layouts from CAESAR II® Neutral files, PCF Files, and GIS shapefiles regardless of source
Comprehensive pump analysis
Model centrifugal and positive displacement pumps with real-world fidelity and evaluate performance under varying operating conditions.
- Model your centrifugal and positive displacement pumps to account for:
- Shifting performance curves through variable speed control and impeller trimming
- Viscosity corrections using standards from the Hydraulic Institute
- Acceleration head loss for positive displacement pumps
- NPSH evaluation
- Size motors and evaluate power usage by considering wire-to-water efficiency (including pump, motor and VFD efficiencies)
- Evaluate Pump and System curve interaction including composite head and efficiency curve

Cost & energy optimization
Balance initial investment with long-term energy consumption by analyzing capital and operational expenses.
- Calculate the capital costs of pipes and components, as well as operating energy expenses
- Wire-to-water efficiency, including pump, motor, and variable frequency drive efficiencies, is used to size motors and evaluate power usage
- Account for heat transfer effects in pipes and heat exchangers

Standards & compliance
Ensure your design adheres to critical regulatory and engineering standards for performance and safety.
- Ensure a design adheres to industry standards such as API 526, ANSI/HI 9.6.3, API 610, or NFPA Standards
- Consider viscosity and frictional effects from non-Newtonian viscosity models or non-settling slurries

Fluids & component libraries
Accelerate model building with built-in databases and optional extensions for fluid property data.
- Leverage built-in libraries of fluids and fittings to build your own database upon
- Built-in libraries of fluids (including NIST REFPROP and ASME Steam Tables) and fittings which can be extended and customized
- An optional Chempak add-on utility provides a thermophysical database of almost 700 fluids

Slurry system modeling
Accurate Hydraulic Analysis for Complex Slurry Flows
- Multi-Component Slurry Modeling
- Support for up to four-component non-settling slurries, enabling detailed simulation of blended mixtures with multiple solids and liquid phases.
- Non-Newtonian Fluid Behavior
- Account for shear-dependent viscosity in slurries using built-in models for shear-thinning and shear-thickening flow conditions.
- Viscosity Corrections & Friction Losses
- Apply Hydraulic Institute methods and empirical correlations to determine accurate pressure drop and energy requirements in slurry pipelines.
- Pump & Piping Sizing with Slurries
- Evaluate the effects of solid concentration and particle behavior on pump performance, NPSH, and optimal pipe diameter selection.

Add-on Modules
Engineering extension tools that can help you quickly and efficiently complete projects. Modules can work individually or together within Fathom and your existing Fathom models.
Models the effects of pumping fluids containing settling solids using the Wilson/GIW method. Used with either Fathom or Impulse.
Identifies input parameters that yield desired output values and simulates control functions. Used with either Fathom or Arrow.
Models dynamic system behavior in steady-state flow and how critical system parameters vary over time. Used with either Fathom or Arrow.
Evaluates the complex interaction of system variables to reveal combinations of cost savings. Used with either Fathom or Arrow.
The Chempak add-on utility provides a thermophysical database of almost 700 liquids and 600 gases with mixing capability.
Helps identify pipe acoustical frequencies to avoid resonance from excitation, especially in systems with positive displacement pumps and reciprocating compressors. Used with either Impulse or xStream
Results

See how the engineer used a pump and system approach to increase capacity, use of features, and use of the model to reveal faults in the physical system.
Learn More
Arrow model was used to identify the configuration with the greatest energy savings across system states
Learn More
Surge potential evaluation of 9 HVAC circuits in an 11-story data center including chilled water, process water, condenser, condensate, and fuel oil circuits.
Learn MoreWho We Serve
Datacor Pipe Flow Modeling is built for professionals who design, analyze, and operate complex fluid systems.
From plant engineers to consulting firms, Datacor Pipe Flow Modeling Solutions empowers users to optimize performance, troubleshoot issues, and ensure safe, efficient operations. If your work depends on understanding and improving piping and fluid flow systems, Datacor is your trusted partner.
Speak with an ExpertQuestions?
How has Fathom been verified?
First, it has been compared to published data where it exists. Available published data is usually for a single pipe, which is not very challenging for a network solver. Models, comparisons and explanations for such published predictions are given in the Verification folder.
Second, it can be verified that predictions agree with the fundamental equations for networks. Finally, predictions have been compared to test data and other analytical methods on numerous occasions and good agreement has been shown.
What is the limit to the size of model I can create with Fathom?
Can I model a non-Newtonian fluid in Fathom?
Can Fathom model ducting system like those in HVAC, ventilation and dust collection systems?
Can Fathom model fire sprinkler systems?
Can I keep all of my design cases together in a single file?
I see cost settings for Material, Installation, Maintenance and Operation. Do I need to specify costs for each one?
No. Depending on your goal, you need only specify the costs for which you are interested. If you are looking for just a first-cost estimate, then you need to only specify Material and possibly Installation. Remember, these are very broad categories and can be tailored to meet your specific application.
Costs are entered in a one or more user-defined Cost Databases using the Cost Database editor. You can keep separate databases for each type of cost or put all the costs for a project into one database. These databases can also be used in multiple models and can be shared among all the users over a network.
You can specify an Interest Rate and an Inflation Rate which are used over the System Life.
Is there a limit on the number of variables and goals Fathom GSC can handle?
Fathom Resources
Explore More Resources








You may also be interested in
Steady-State Compressible Flow Modeling. Calculate pressure drop and flow distribution in gas and steam systems
Surge analysis software used to calculate high-pressure transients in liquid piping systems caused by water hammer.
dynamic simulation tool for high-speed, acoustic transients that occur in steam and gas piping systems.
Robust chemical process simulation software designed to meet the diverse needs of engineers who design, troubleshoot, and innovate.